Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is the term often given for a narrow complex tachycardia with no identifiable P waves. However, SVT is a general term for a group of arrhythmia with the impulse originating above (supra - Latin for above) the ventricles which could either be the sinus node, atria, AV node or the bundle of His.
SVT can however have a wide QRS. This can be due to a preexisting bundle branch block or intraventricular conduction delay, aberrancy or preexcitation.
Simplified Approach
Several authors have a different approach for tachyarrhythmia. Here is a simple approach. Tachycardia can be classified based on 3 questions:
- Is the tachycardia Regular or irregular?
- Is it a Narrow QRS complex (< 0.12 sec) or Wide QRS complex (≥ 0.12 sec)?
- Is it a short-RP or long RP tachycardia?
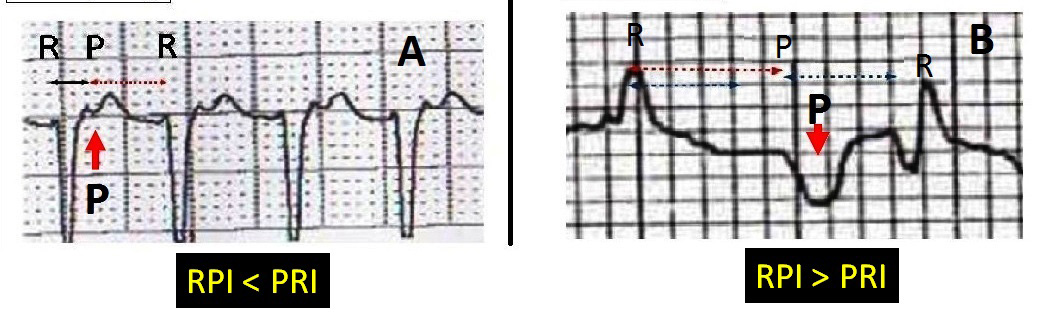
RP interval
The RP interval (RPI) is measured from the beginning of the QRS complex to be beginning of the P wave. The PR interval (PRI) is measured from the beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complex. Comparing the RPI to PRI will create two big groups of SVT. If the RP interval is shorter than the PRI interval then a SVT is called short RP tachycardia. If the RP interval is longer than the PRI then it is called long RP tachycardia.
Short RP vs Long RP. Image A is a short RP tachycardia. The RP interval is shorter than the PRI. Image B is a long RP tachycardia. The RP interval is longer than the PRI.
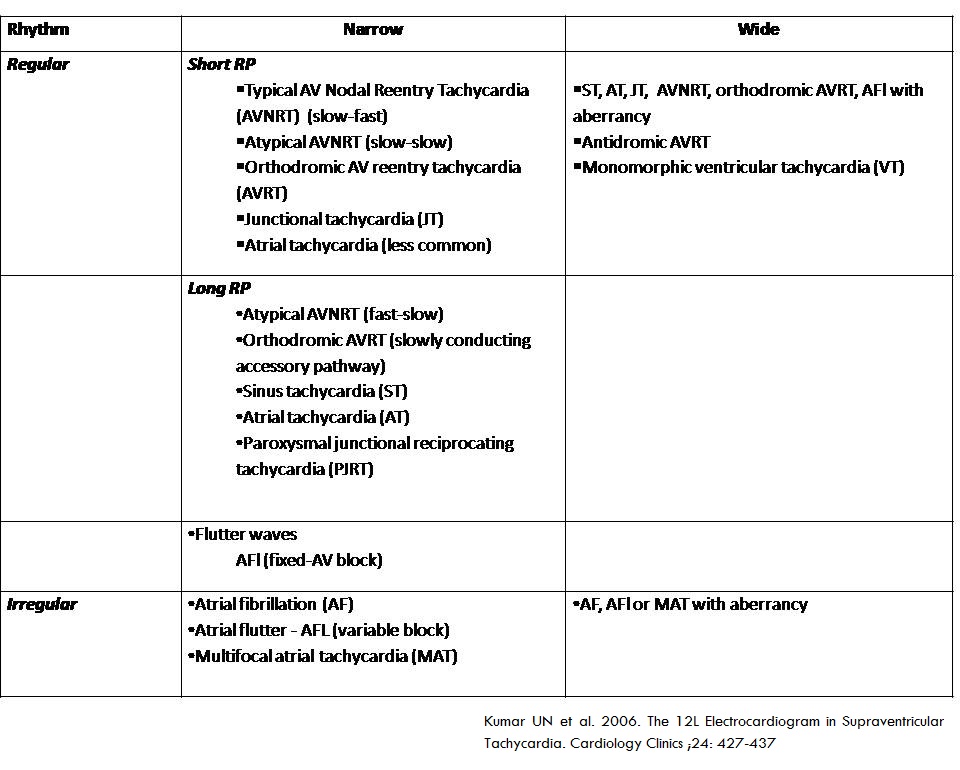
Based on the 3 questions, SVT's are classified below. This will narrow-down the diagnosis.
Simplified SVT classification
Sinus tachycardia I(ST) and atrial tachycardia (AT) utilizes the AV node for anterograde (atrium to ventricles) conduction generates a short PRI and long RPI. So, sinus tachycardia and atrial tachycardia are long RP tachycardia. AT can also be short RP tachycardia when there is delayed AV conduction.
Diagram for the Different SVT. (adapted from Braunwald's Textbook of Cardiology)


No comments:
Post a Comment